Python is known for its simplicity and readability, but its true power lies in its extensive collection of libraries, packages, and modules. These tools allow developers to perform a wide range of tasks efficiently. This tutorial will cover the following topics:
- Understanding Libraries, Packages, and Modules
- Importing Packages and Modules
- Overview of Popular Python Libraries
1. Understanding Libraries, Packages, and Modules
Modules: A module is a single file (or files) that are imported under one import and used. They are usually Python files that contain functions, classes, and variables. Modules help in organizing code logically.
Packages: A package is a collection of modules. It is a directory that contains a special file named __init__.py and can have sub-packages and modules.
Libraries: A library is a collection of related modules and packages that provide specific functionalities.
Example:
- Module:
math.py(a file containing mathematical functions). - Package:
mypackage(a directory containing multiple modules and possibly sub-packages). - Library:
NumPy(a collection of modules and packages for numerical computation).
2. Importing Packages and Modules
Importing is the process of bringing a module or package into your current script to use its functions, classes, or variables.
Importing a Module

Importing Specific Functions or Classes from a Module
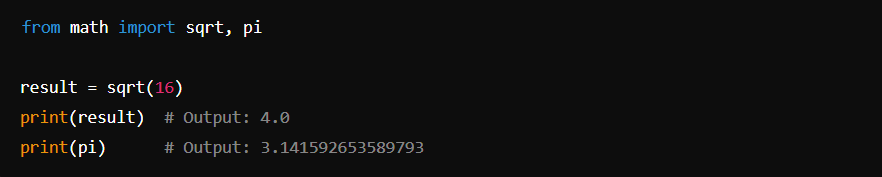
Importing a Package
Packages are imported similarly to modules. You can import specific modules from a package.

Importing with an Alias
Using aliases can make code cleaner and prevent naming conflicts.

3. Overview of Popular Python Libraries
NumPy
NumPy is the fundamental package for numerical computing in Python. It provides support for arrays, matrices, and many mathematical functions.
Installation: pip install numpy
Basic Usage:
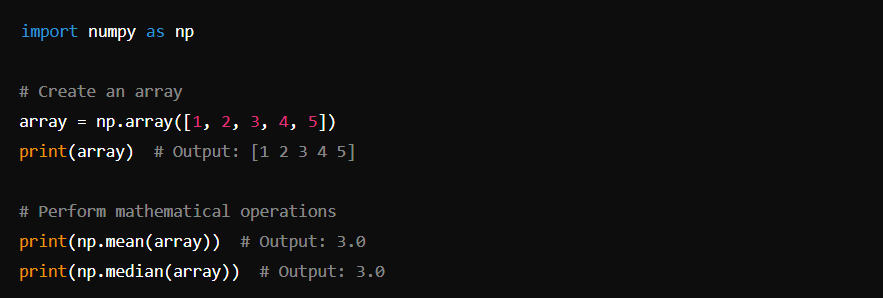
Pandas
Pandas is a powerful library for data manipulation and analysis. It provides data structures like Series and DataFrame.
Installation: pip install pandas
Basic Usage:
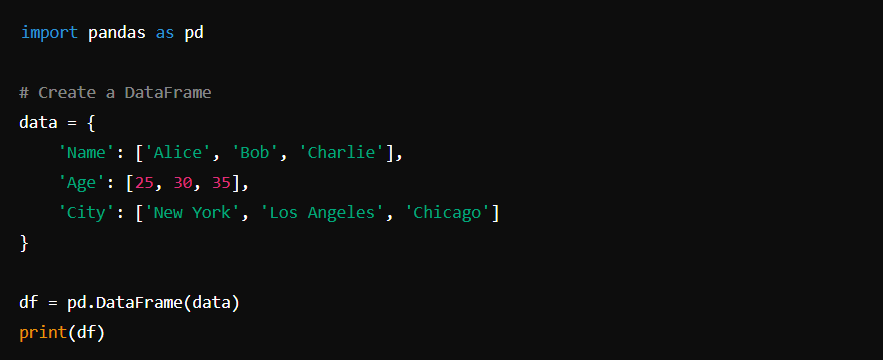
Matplotlib
Matplotlib is a plotting library for creating static, animated, and interactive visualizations in Python.
Installation: pip install matplotlib
Basic Usage:
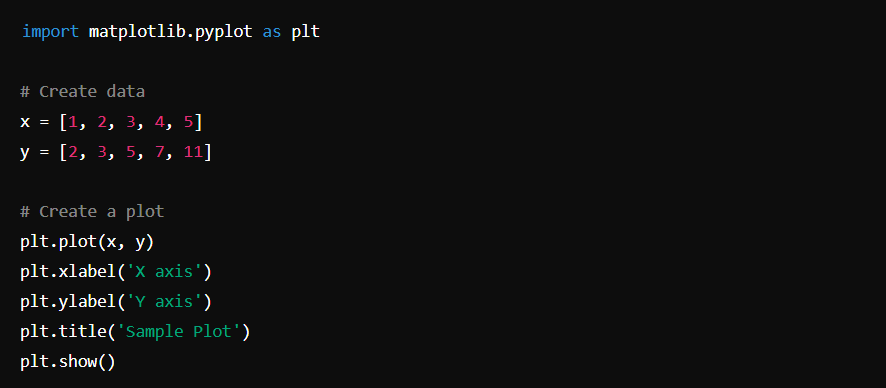
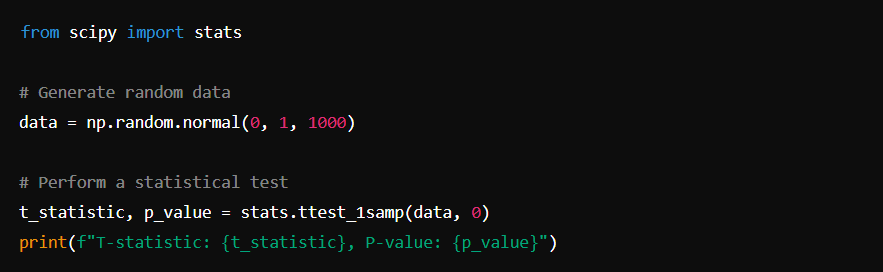
SciPy
SciPy is a library used for scientific and technical computing. It builds on NumPy and provides additional functionality.
Installation: pip install scipy
Basic Usage:
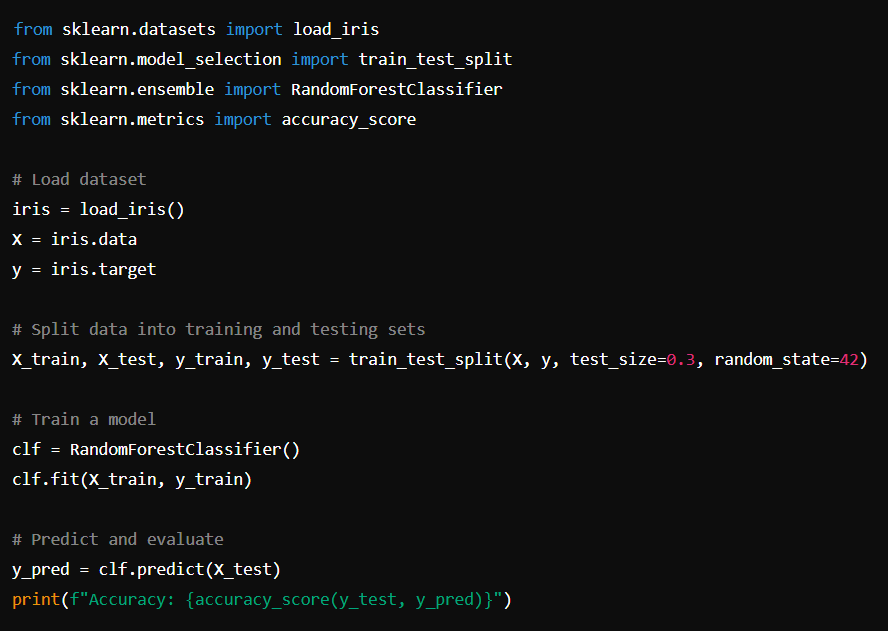
Scikit-Learn
Scikit-Learn is a machine learning library that provides simple and efficient tools for data mining and data analysis.
Installation: pip install scikit-learn
Basic Usage:
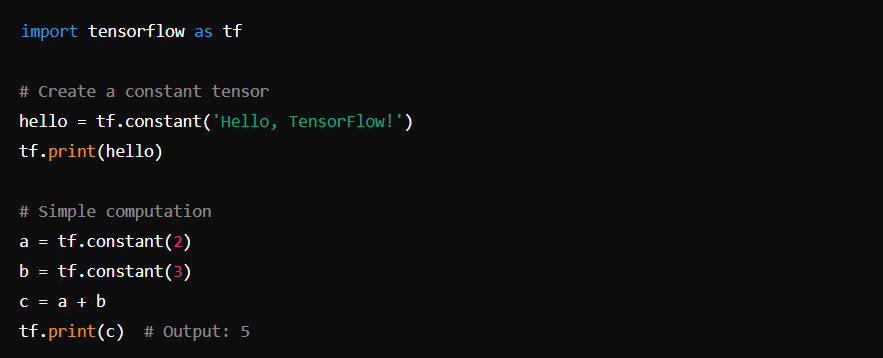
TensorFlow
TensorFlow is an open-source library for machine learning and deep learning developed by Google.
Installation: pip install tensorflow
Basic Usage:
Flask
Flask is a micro web framework for building web applications in Python.
Installation: pip install flask
Basic Usage:

Django
Django is a high-level web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design.
Installation: pip install django
Basic Usage:

Conclusion
This tutorial provided an overview of Python libraries, packages, and modules, including how to import and use them. It also introduced some of the most popular Python libraries used for various tasks, such as numerical computation, data analysis, visualization, scientific computing, machine learning, and web development. With this foundation, you can start exploring these tools and harness their power in your Python projects.